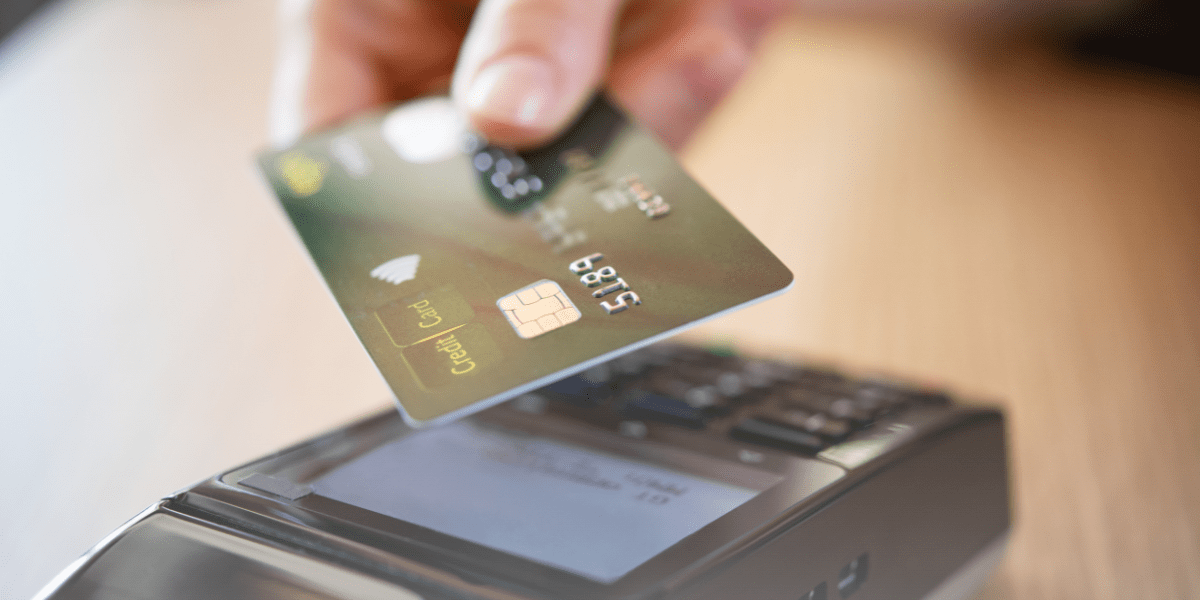
Accepting credit card payments is essential for small businesses looking to expand their customer base and improve cash flow. With the rise of digital payments, providing a variety of payment options not only meets customer expectations but also enhances the overall shopping experience. In this guide, we'll walk you through everything you need to know about how to take credit card payments, including the steps to get started, the different methods available, and the factors to consider when choosing a payment processor.
Why Accept Credit Card Payments?
Before diving into the technicalities of how to take credit card payments, it's important to understand why accepting credit cards is beneficial for your business:
- Increased Sales: Customers are more likely to make a purchase if they can use their preferred payment method. Credit cards often lead to higher transaction amounts compared to cash payments.
- Improved Cash Flow: Credit card transactions are processed quickly, with funds typically deposited into your business account within a few days, improving your cash flow.
- Enhanced Security: Accepting credit cards reduces the need to handle cash, which minimizes the risk of theft and errors.
Steps to Start Accepting Credit Card Payments
To start accepting credit card payments, follow these steps:
1. Choose How You’ll Accept Payments
There are several ways to accept credit card payments, depending on your business model:
- In-Person Payments: If you run a brick-and-mortar store, you'll need a point-of-sale (POS) system that includes a card reader for swiping, dipping, or tapping credit cards.
- Online Payments: For eCommerce businesses, an online payment gateway integrated with your website is essential. This allows customers to enter their card details securely during checkout.
- Mobile Payments: For businesses on the go, such as food trucks or service providers, mobile card readers that connect to your smartphone or tablet are ideal.
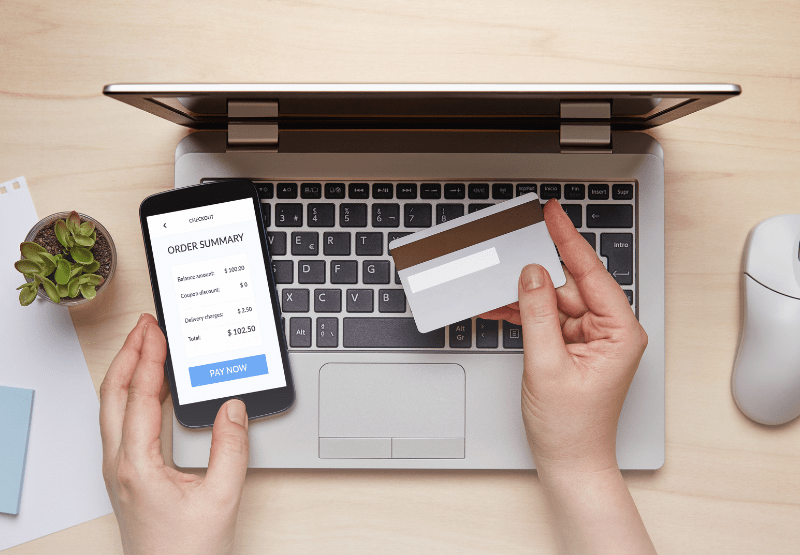

2. Select a Merchant Service Provider
A merchant service provider (MSP) enables your business to process credit card payments. When choosing an MSP, consider factors such as:
- Fees: Look for a provider that offers competitive transaction fees and transparent pricing models.
- Security: Ensure the MSP complies with PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) to protect your customers' data.
- Integration: Choose an MSP that easily integrates with your existing systems, whether it's your POS system or eCommerce platform.
3. Open a Merchant Account
A merchant account is necessary for processing credit card payments. It acts as an intermediary holding account where funds from transactions are deposited before being transferred to your business account. Some payment processors offer merchant accounts as part of their service, while others require you to set one up separately.
4. Set Up Your Payment Processing System
Depending on how you plan to accept payments, you’ll need to set up your payment processing system:
- POS System: For in-person transactions, install a POS system with a card reader. Ensure it supports various payment methods, including chip cards, magnetic stripe cards, and contactless payments.
- Payment Gateway: For online transactions, integrate a payment gateway with your website. This gateway securely captures and encrypts the card information before processing it through your payment processor.
- Mobile Payment System: For mobile payments, download the necessary app and connect it to a mobile card reader.
How Do I Accept Credit Card Payments Online?
Accepting credit card payments online is a critical component for any eCommerce business. It enables customers to make secure and convenient purchases from anywhere, which can significantly increase your sales and broaden your customer base. Here’s an expanded look at the essential steps involved:
1. Create a Digital Storefront
The first step to accepting credit card payments online is establishing a digital storefront. If you don’t already have a website, you’ll need to create one using a website builder or eCommerce platform. Here’s how you can go about it:
- Website Builders: Platforms like Wix, Squarespace, and Weebly allow you to create a website without needing any coding knowledge. They offer drag-and-drop interfaces and customizable templates, making it easy to design a professional-looking site quickly.
- eCommerce Platforms: If you’re specifically looking to sell products online, using an eCommerce platform like Shopify, WooCommerce (for WordPress), or BigCommerce might be the best option. These platforms are designed with online selling in mind, providing built-in features for managing products, inventory, orders, and payments.
Your digital storefront should be user-friendly, visually appealing, and optimized for mobile devices. Make sure the checkout process is straightforward to minimize cart abandonment.
2. Integrate a Payment Gateway
Once your website is up and running, the next step is to integrate a payment gateway. A payment gateway is a crucial piece of technology that acts as a bridge between your website and the financial institutions involved in the transaction. Here’s how to choose and integrate one:
- Choosing a Payment Gateway: There are many payment gateways available, such as PayPal, Stripe, and Authorize.Net. When selecting a gateway, consider factors like transaction fees, compatibility with your eCommerce platform, and the payment methods it supports (e.g., credit/debit cards, mobile wallets). Some platforms, like Shopify, come with their own integrated payment gateways, making the setup process easier.
- Integration Process: The integration process can vary depending on the payment gateway and the platform you’re using. Most modern eCommerce platforms offer plugins or modules that make integration straightforward. For instance, if you’re using WordPress with WooCommerce, you can easily add a payment gateway like Stripe by installing the corresponding plugin.
Once integrated, the payment gateway will handle the secure transmission of credit card details from the customer to the payment processor. The gateway encrypts sensitive data, such as card numbers and CVVs, ensuring that this information remains protected throughout the transaction process.
3. Ensure PCI Compliance
Security is paramount when accepting credit card payments online. To protect your customers' sensitive information and avoid potential breaches, your payment processing solution must be compliant with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Here’s what that entails:
- Understanding PCI Compliance: PCI DSS is a set of security standards designed to ensure that all companies that process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment. Compliance is mandatory for all businesses that accept credit card payments.
- Achieving Compliance: The level of PCI compliance required depends on your business size and the volume of transactions you process. For small businesses, compliance might involve completing a Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) and undergoing a vulnerability scan by an Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV). If you’re using a third-party payment processor or gateway, they often handle most of the compliance requirements, but you still need to ensure that your website and hosting environment are secure.
- Maintaining Compliance: PCI compliance is not a one-time task; it requires ongoing maintenance. This includes regularly updating your software, applying security patches, conducting periodic vulnerability scans, and educating your staff about best practices in payment security.
By following these steps, you can effectively set up your online business to accept credit card payments securely and efficiently. This not only helps you meet customer expectations but also protects your business from potential security breaches and financial penalties associated with non-compliance.
Understanding Credit Card Processing Fees
When accepting credit card payments, it's important to understand the fees involved:
- Transaction Fees: Typically range from 1.5% to 3.5% of the transaction amount, depending on the type of card and the payment processor.
- Interchange Fees: Paid by the merchant to the cardholder's bank, these fees vary based on the card type and transaction method.
- Monthly Fees: Some MSPs charge a monthly fee for account maintenance and additional services like fraud protection.
Tips for Choosing the Right Payment Processor
When selecting a payment processor, consider the following:
- Compatibility: Ensure the processor integrates smoothly with your existing systems.
- Support: Look for a provider that offers robust customer support, ideally 24/7, to help with any issues that arise.
- Scalability: Choose a solution that can grow with your business, handling increased transaction volumes as needed.
Knowing how to take credit card payments effectively is crucial for small businesses looking to compete in today's market. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can set up a seamless and secure payment process that meets your customers' needs and supports your business's growth. Whether you're accepting payments in-person, online, or on the go, the right tools and strategies will ensure that your payment process is efficient and reliable.
Key Takeaways
- Importance of Accepting Credit Cards: Accepting credit card payments is essential for increasing sales, improving cash flow, and providing a secure transaction process for your customers.
- Choosing a Payment Processor: Selecting the right merchant service provider (MSP) is crucial for ensuring competitive fees, strong security measures, and seamless integration with your existing systems.
- Setting Up Payment Systems: Whether you're accepting payments in-person, online, or through mobile devices, it's important to choose the appropriate setup that aligns with your business needs.
- Understanding Online Payment Processing: For eCommerce businesses, integrating a secure payment gateway and ensuring PCI compliance is key to protecting customer data and maintaining trust.
- Managing Credit Card Processing Fees: Be aware of the various fees involved in credit card processing, including transaction fees, interchange fees, and monthly maintenance costs, to better manage your business expenses.
Author Profile
Moneris Team
Author Profile
Moneris is a leading provider of payment processing solutions in Canada. Our blog is your go-to resource for insights into the ever-evolving world of payments. We cover everything from the latest industry trends and technologies to practical advice for businesses of all sizes. Our blog's mission is to spotlight small businesses and provide resources that help them succeed in today's economy. Blog articles are written by members of Moneris' in-house marketing team with support from internal product and industry experts.